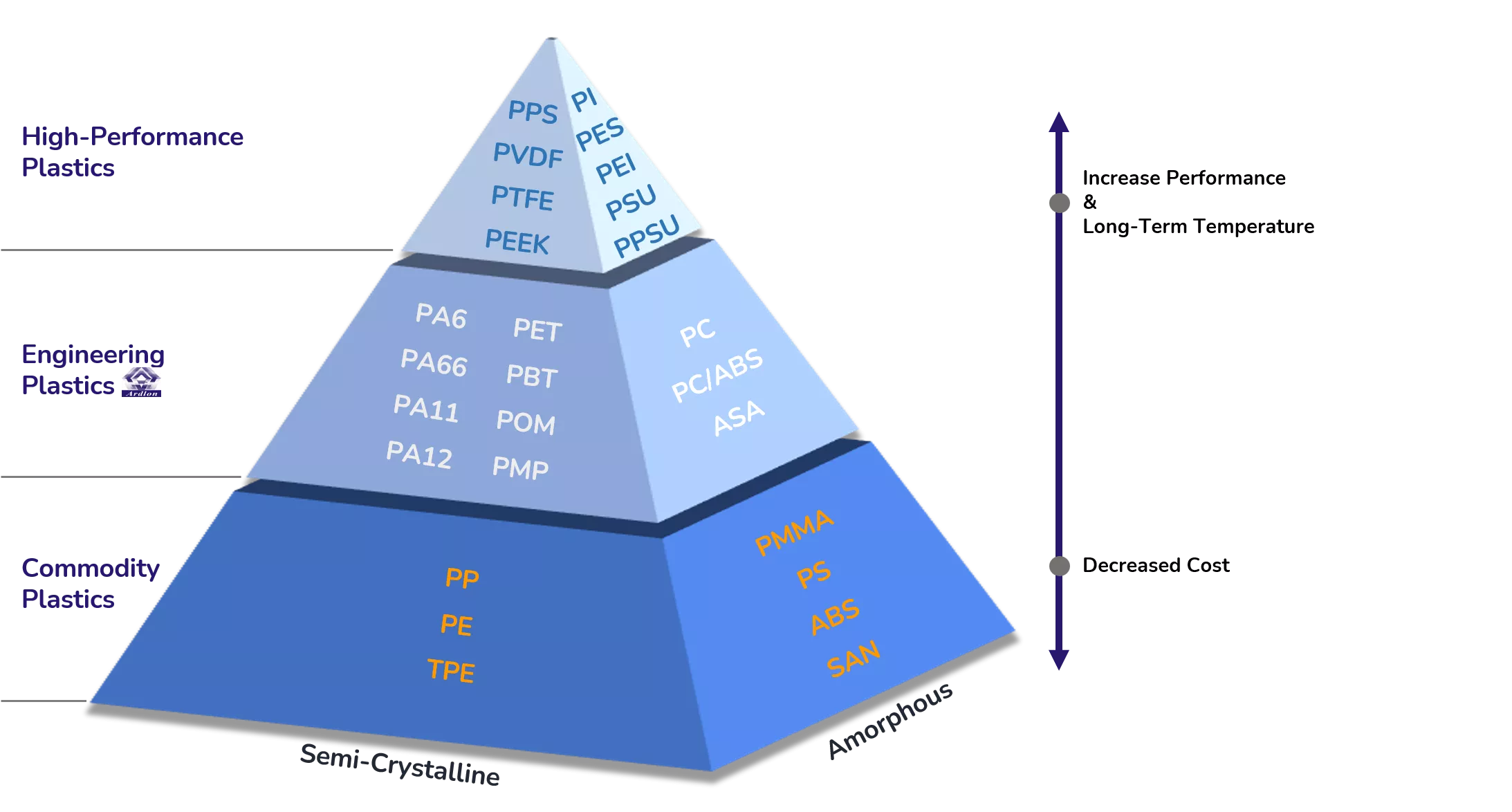
High-Performance Polyamides: PA46, PA6I, PA6T, and PA9T Comparison Guide
High-performance polyamides (HPPAs) are a specialized class of engineering thermoplastics designed for extreme operating conditions — far beyond what standard nylons like PA6 or PA66 can endure. Unlike conventional aliphatic polyamides, HPPAs incorporate aromatic components into their molecular backbone, enhancing their thermal resistance, mechanical rigidity, and chemical durability.
Common high-performance polyamides include PA46, PA6I, PA6T, and PA9T. These materials are widely used in automotive, electronics, and industrial applications where dimensional stability, soldering resistance, or fuel exposure are key requirements.
In this guide, we'll compare the structures, properties, and applications of four widely used HPPAs to help you make the right material decision.
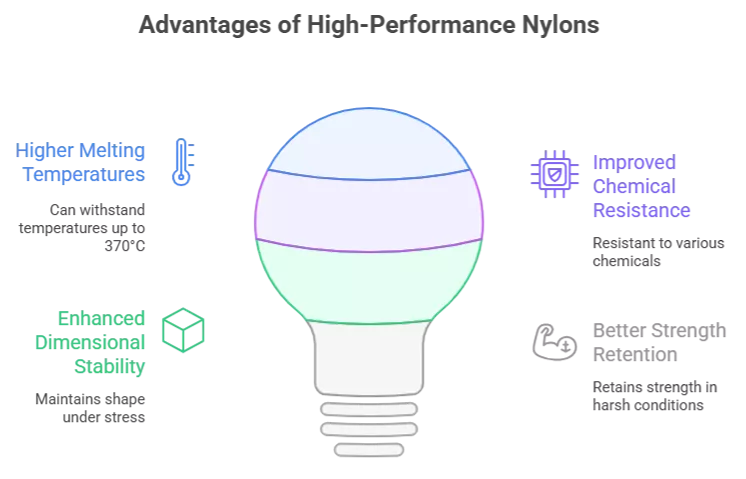
Quick Overview: What Are High-Performance Nylons?
High-performance nylons are engineered thermoplastics based on modified polyamide structures, offering:
- Higher melting temperatures (up to 370°C)
- Improved chemical resistance
- Enhanced dimensional stability
- Better strength retention in hot and humid environments
These grades are ideal for demanding applications in automotive, electronics, industrial, and chemical environments.
📌 PA46 (Polyamide 46)
What Is PA46?
PA46, also known as Polyamide 46, is made from tetramethylene diamine and adipic acid. It offers a very high crystallinity and fast crystallization rate, making it excellent for precision molding.
Key Features of PA46:
- Melting point: ~295°C
- Excellent wear and friction resistance
- High dimensional stability
- Superior resistance to creep
Common Applications of PA46:
- Automotive under-the-hood parts
- Electrical connectors
- Gear wheels and bearings
📌 PA6I (Polyamide 6I)
What Is PA6I?
PA6I is a semi-aromatic polyamide formed from hexamethylenediamine and isophthalic acid. It's often used in copolymer blends for better processability.
Key Features of PA6I:
- High Tg (~130–150°C)
- Lower moisture absorption than PA66
- High chemical resistance
- Stable mechanical properties under heat
Applications of PA6I:
- Electrical/electronic components
- LED housing
- Precision connectors
📌 PA6T (Polyamide 6T)
What Is PA6T?
Among high-performance polyamides, PA6T stands out as a semi-aromatic variant synthesized from hexamethylenediamine and terephthalic acid.
Key Features of PA6T:
- Melting point: ~370°C (depending on copolymer type)
- Excellent dimensional accuracy
- Great soldering resistance
- UL94 V-0 flame rating in many grades
Applications of PA6T:
- SMT (surface-mount technology) components
- Automotive engine components
- Chemical pump housings
📌 PA9T (Polyamide 9T)
What Is PA9T?
PA9T is a high-performance semi-aromatic polyamide that balances excellent processability with low water absorption and electrical insulation stability.
Key Features:
- Melting point: ~295°C
- Very low water absorption
- High CTI (comparative tracking index)
- Strong resistance to automotive fluids and fuels
Applications:
- High-temperature connectors
- Electric vehicle (EV) components
- Fuel system parts
- E&E modules
🔄 Comparison Table: PA46 vs PA6I vs PA6T vs PA9T
The following table compares four major high-performance polyamides—PA46, PA6I, PA6T, and PA9T—across essential performance metrics including melting point, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability.
| Property | PA46 | PA6I | PA6T | PA9T |
| Melting Point (°C) | ~295 | ~150 (Tg) | ~370 | ~295 |
| Moisture Absorption | Medium | Low | Low | Very Low |
| Processability | Excellent | Good | Fair | Good |
| Heat Resistance | High | Medium | Very High | High |
| Dimensional Stability | High | High | Very High | Very High |
| Common Use Case | Gears, E&E | Connectors | SMT, Auto | EV, Fuel Sys |
As the comparison shows, each high-performance polyamide offers unique trade-offs between thermal stability, moisture resistance, and ease of processing — all of which are crucial for material selection in engineering applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is PA46 better than PA66?
Yes — in terms of heat resistance and dimensional stability. PA46 performs better under high temperatures and has higher wear resistance than standard PA66.
What is the difference between PA6T and PA9T?
PA6T has higher heat resistance, while PA9T offers better moisture resistance and easier processability. PA6T is ideal for SMT components; PA9T is preferred for E&E and fuel system parts.
Is PA6I suitable for high-temperature applications?
PA6I has a high glass transition temperature (~150°C) but lower than PA6T or PA9T. It is best suited for moderate heat resistance and superior chemical performance.
Are high-performance polyamides recyclable?
Some grades are recyclable depending on the additives and processing. However, their semi-aromatic structures make recycling more challenging than standard nylons like PA6/66.
What are high-performance polyamides used for?
They are used in critical applications that require high heat resistance, low moisture uptake, and long-term dimensional stability. Examples: SMT electronic components, EV connectors, automotive engine parts, and precision gears.
High-Performance Polyamide Market Outlook
The market for high-performance polyamides is growing steadily, driven by increasing demand from automotive, electrical & electronics (E&E), and EV sectors. Materials like PA6T and PA9T are seeing rapid adoption due to their ability to withstand high temperatures, maintain dimensional stability, and resist moisture—making them ideal for SMT components, EV connectors, and fuel systems.
Asia remains the largest consumer region, with Japan, South Korea, and China leading production and usage. Global suppliers such as Envalior, Kuraray, and EMS are expanding their HPPA portfolios to meet the performance and regulatory needs of next-generation applications.
As EV penetration and miniaturized electronics continue to rise, the need for reliable, low-absorption, flame-retardant polyamides is expected to accelerate. In particular, PA9T is gaining momentum due to its processability and stable supply.
For businesses seeking to stay ahead in design and procurement, understanding these material trends is just as critical as knowing technical specs.

Structural Differences: Why PA46, PA6I, PA6T, and PA9T Perform Differently
The numbers and letters in polyamide names like PA46, PA6I, PA6T, and PA9T refer to the chemical structure of their monomers — specifically, the number of carbon atoms in the diamine and diacid components used to synthesize the polymer.
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- PA46: Tetramethylene diamine (4C) + Adipic acid (6C)
- PA6I: Hexamethylene diamine (6C) + Isophthalic acid (aromatic, meta)
- PA6T: Hexamethylene diamine (6C) + Terephthalic acid (aromatic, para)
- PA9T: Nonamethylene diamine (9C) + Terephthalic acid (aromatic, para)
Chain Length, Crystallinity & Melting Point
Generally, longer aliphatic chains reduce crystallinity and melting point but improve flexibility and reduce moisture absorption. Aromatic content increases thermal resistance but can hinder flowability.
| Material | Chain Structure | Aromatic Content | Crystallinity | Melting Point |
| PA46 | Aliphatic (4,6) | None | Very High | ~295°C |
| PA6I | (6, Isophthalic) | Moderate (meta) | Low | No sharp melt |
| PA6T | (6, Terephthalic) | High (para) | Medium | ~370°C |
| PA9T | (9, Terephthalic) | High (para) | Medium | ~295°C |
📌 Understanding the molecular structure helps explain why certain HPPAs outperform others in molding behavior — particularly PA6T and PA6I, which are often compared in electronic connector applications.
🏠 Why PA6T Has Better Flowability Than PA6I
Although both PA6I and PA6T are semi-aromatic nylons, PA6T generally offers better flowability due to:
- Faster Crystallization: Para-substituted terephthalic acid in PA6T promotes easier chain alignment and faster solidification.
- Copolymer Blends: PA6T is often modified with PA66 segments, reducing melt viscosity for better injection moldability.
- PA6I, with meta-substitution, introduces irregularities into the chain, lowering crystallinity and slowing down the molding process.
Key Takeaways: Structural Trade-Offs Between PA6T, PA6I, and PA9T
| Material | Key Features | Flowability | Crystallization | Moisture Absorption | Melting Point |
| PA6T | Highest rigidity and thermal resistance | Lower (higher viscosity) | Fast (may cause warpage) | Low | ~370°C |
| PA6I | Balanced version of PA6T, improved moldability | Better than PA6T | Slower (reduces warpage) | Lower than PA6T | ~150–160°C |
| PA9T | Lowest moisture absorption and best dimensional stability | Good | Moderate | Very Low | ~295°C |
Based on internal testing across over 50 custom formulations, we observed that PA6T maintained dimensional stability after 3 cycles of 260°C reflow soldering, while PA9T showed the least moisture-induced expansion over 72-hour high humidity exposure.
📌 Rule of Thumb:
The longer the carbon chain in the diamine (e.g., PA9T vs. PA6T), the lower the moisture absorption — but also the lower the crystallinity and melting point.
This is why PA6T remains the preferred choice for high-temperature reflow soldering, while PA9T shines in humid or dimension-critical environments like EV connectors and E&E modules.
These structure–property relationships form the foundation for making informed material choices in real-world engineering environments.
Need an HPPA Alternative? (PA46, PA6I, PA6T, PA9T)
We can help you meet equivalent performance targets using engineered alternatives from our portfolio:
- PA66 GF/CF & impact-modified grades — higher stiffness/strength, heat resistance, and shock absorption.
- Low-moisture nylon compounds — improved dimensional stability in humid environments.
- Long Carbon Fiber Composites — high CTI, electrical insulation, and stable mechanicals at temperature.
- GF & mineral-filled PA — warp control and precision for tight-tolerance parts.
- PP GF — chemical resistance and weight/cost advantages for non-high-heat parts.
- Recycled / toughened PA — sustainability without major performance compromise.
Contact us with your operating temperature, environment, and tolerance targets — we’ll recommend viable drop-in candidates and samples.
Explore related resources: Engineering Plastics Guide · PA Compounding & Additives · Glass Fiber Reinforced PA · GF & Mineral-Filled PA · Plastics for Metal Replacement
Selecting the right high-performance polyamide depends on your operating temperature, chemical environment, and dimensional requirements. Whether you need PA6T for reflow soldering or PA9T for EV modules, these advanced materials offer long-term performance advantages over conventional nylons.
👉 Contact us now to discuss your project or request a free sample.

